On-line force capability evaluation based on efficient polytope vertex search
by Antun Skuric, Vincent Padois, David Daney
Published in IEEE ICRA 2021-International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2021
New on-line polytope vertex search algorithm optimised for force and velocity polytope evaluation of serial robots.

Paper abstract
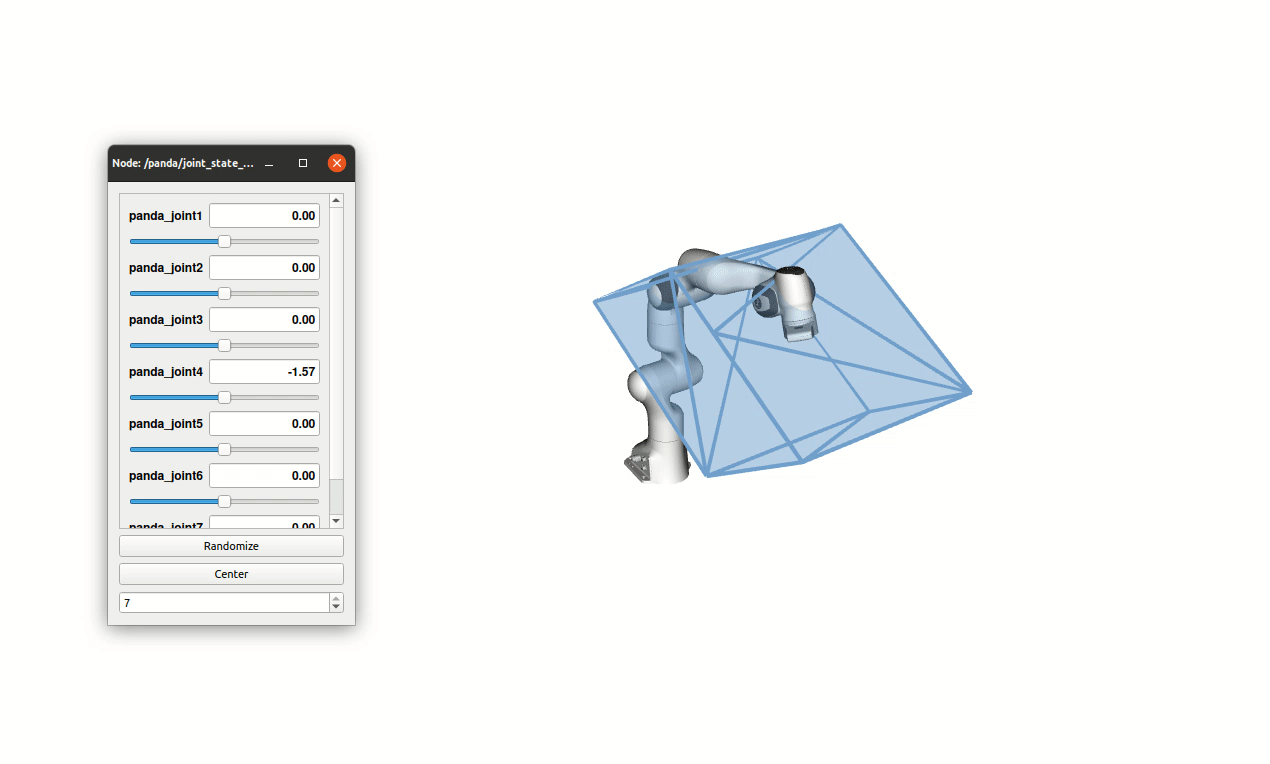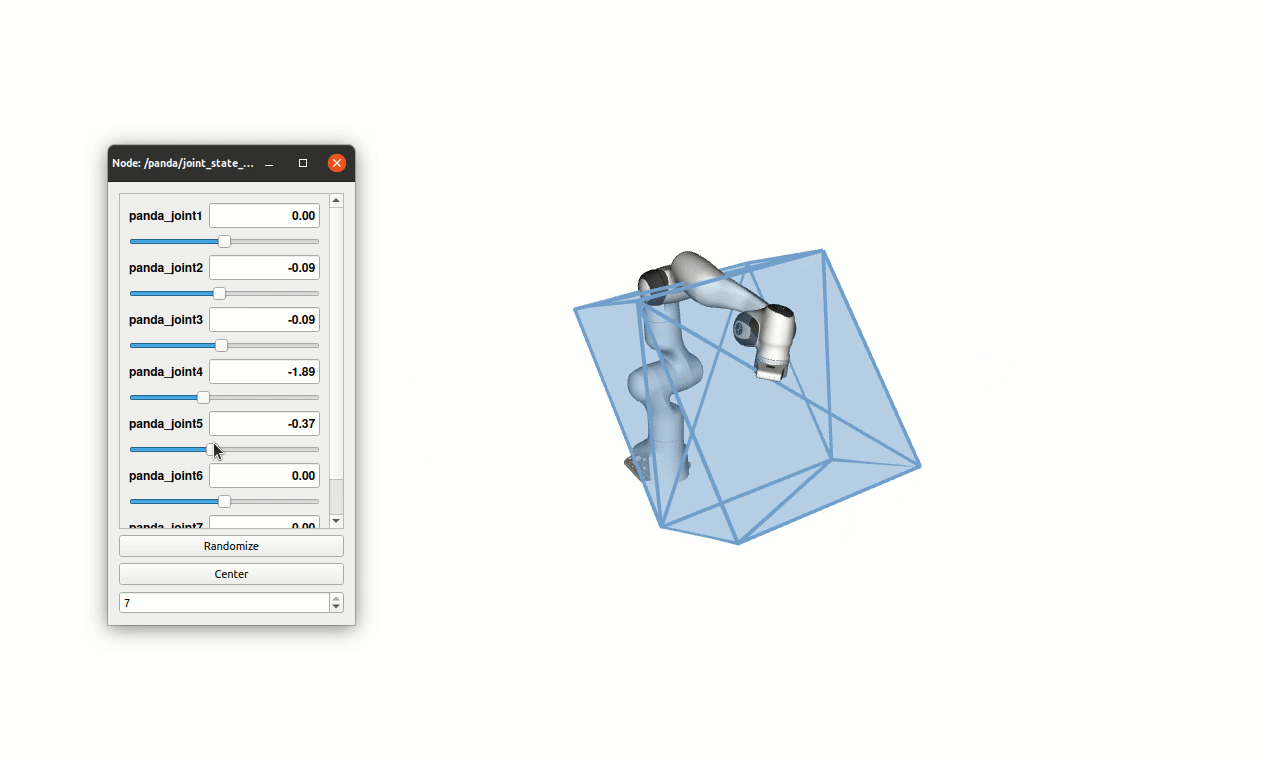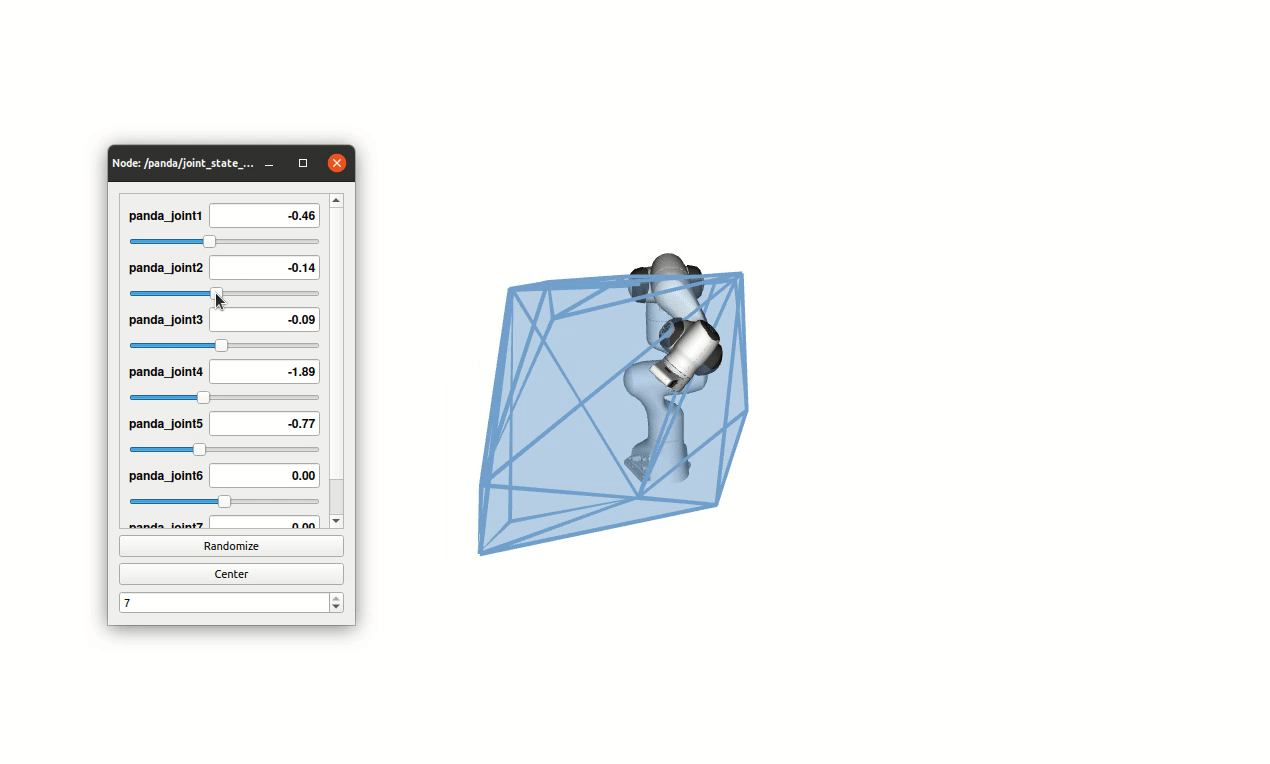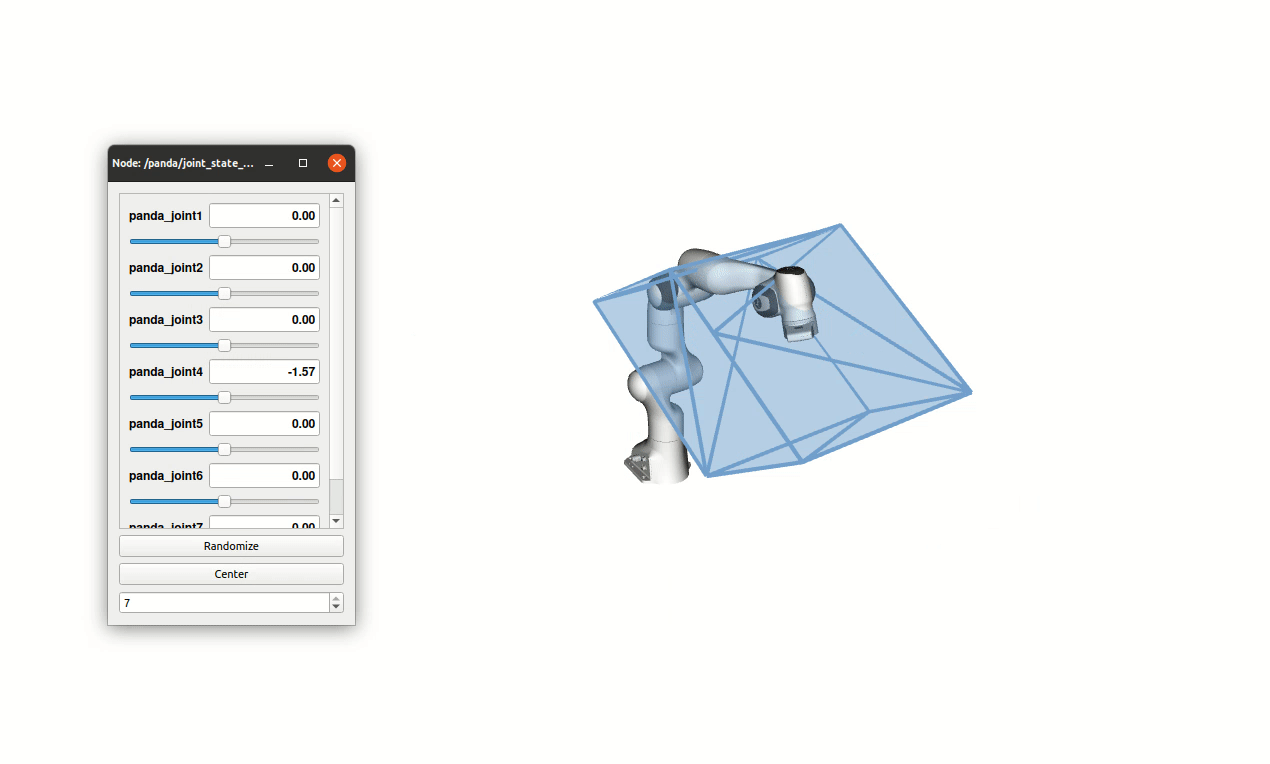
Ellipsoid-based manipulability measures are often used to characterize the force/velocity task-space capabilities of robots. While computationally simple, this approach largely approximate and underestimate the true capabilities. Force/velocity polytopes appear to be a more appropriate representation to characterize the robot’s task-space capabilities. However, due to the computational complexity of the associated vertex search problem, the polytope approach is mostly restricted to offline use, e.g. as a tool aiding robot mechanical design, robot placement in work-space and offline trajectory planning. In this paper, a novel on-line polytope vertex search algorithm is proposed. It exploits the parallelotope geometry of actuator constraints. The proposed algorithm significantly reduces the complexity and computation time of the vertex search problem in comparison to commonly used algorithms. In order to highlight the on-line capability of the proposed algorithm and its potential for robot control, a challenging experiment with two collaborating Franka Emika Panda robots, carrying a load of 12 kilograms, is proposed. In this experiment, the load distribution is adapted on-line, as a function of the configuration dependant task-space force capability of each robot, in order to avoid, as much as possible, the saturation of their capacity.
Video presentation
Getting started
Matlab and python code and more documentation about practical implementation of this method can be found on our gitlab.
Additionally the full algorithm has been implemented in the python pip package pycapacity which enables calculating different task-space capacity metrics for robots and human manipulators in real-time.
pip install pycapacity
Example code
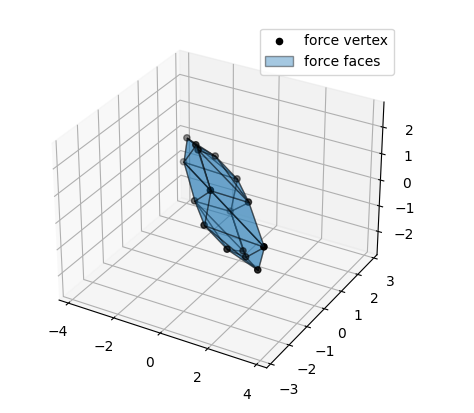
Example code for randomised robot force polytope evaluation using the pycapacity package
"""
A simple example program for 3d force polytope
"""
import pycapacity.robot as capacity # robot capacity module
import numpy as np
m = 3 # 3d forces
n = 6 # robot dof
# this seed is used to generate the same image
# as in the examples in the docs
np.random.seed(12345)
J = np.array(np.random.rand(m,n)) # random jacobian matrix
t_max = np.ones(n) # joint torque limits max and min
t_min = -np.ones(n)
f_poly = capacity.force_polytope(J,t_min, t_max) # calculate the polytope
print(f_poly.vertices) # display the vertices
# plotting the polytope
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pycapacity.visual import * # pycapacity visualisation tools
fig = plt.figure(4)
# draw faces and vertices
plot_polytope(plot=plt,
polytope=f_poly,
label='force',
edge_color='black',
alpha = 0.4)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
The output of the code above is the following